The educational landscape stands at the precipice of a technological revolution. Traditional classroom models, while foundational, are increasingly insufficient to meet the complex demands of modern learning environments. Simulation-based education represents a paradigm shift that transforms abstract concepts into tangible, interactive experiences, fundamentally altering how knowledge is acquired, retained, and applied across diverse educational sectors.
Research consistently demonstrates that learners engaged with simulation-based learning retain information significantly better than those using conventional educational approaches. This enhanced effectiveness stems from the immersive nature of simulations, which stimulate multiple senses simultaneously and create multi-modal learning experiences that engage different cognitive processing centers.
The Science Behind Enhanced Learning Effectiveness
The superiority of simulation-based learning over traditional methods is rooted in cognitive science principles that govern how humans process and retain information. Unlike passive learning methods such as lectures or textbook reading, simulations require active participation, compelling learners to engage with material through critical thinking and direct interaction rather than passive observation.

The accessibility factor further amplifies learning effectiveness. Online simulations operate continuously, allowing learners to engage with educational content according to their individual schedules and learning preferences. This flexibility proves particularly valuable for non-traditional students, working professionals, and adult learners who cannot accommodate rigid class schedules.
Neurological research indicates that experiential learning through simulation activates multiple brain regions simultaneously, creating stronger neural pathways and improving long-term retention. The combination of visual, auditory, and kinesthetic elements in simulation environments stimulates diverse learning modalities, accommodating various learning styles within a single educational framework.
Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Development
Simulation-based education excels in fostering critical thinking capabilities by placing learners in realistic scenarios requiring assessment, decision-making, and problem-solving under guided conditions. This approach proves particularly valuable in professional fields such as healthcare, business management, and military training, where rapid decision-making and sound judgment represent essential competencies.
The experiential learning component enables students to make mistakes and experience consequences within secure environments. This safe space for trial and error allows learners to develop skills confidently, leading to deeper comprehension and stronger personal accomplishment. The iterative nature of simulation-based learning permits multiple attempts at complex problems, reinforcing learning through repetition and variation.
Studies indicate that professionals trained through simulation methods demonstrate superior performance in real-world applications compared to those trained through traditional methods. This improvement stems from the realistic nature of simulated environments, which closely mirror actual working conditions and challenges.
Industry Applications and Real-World Impact
Healthcare and Medical Training
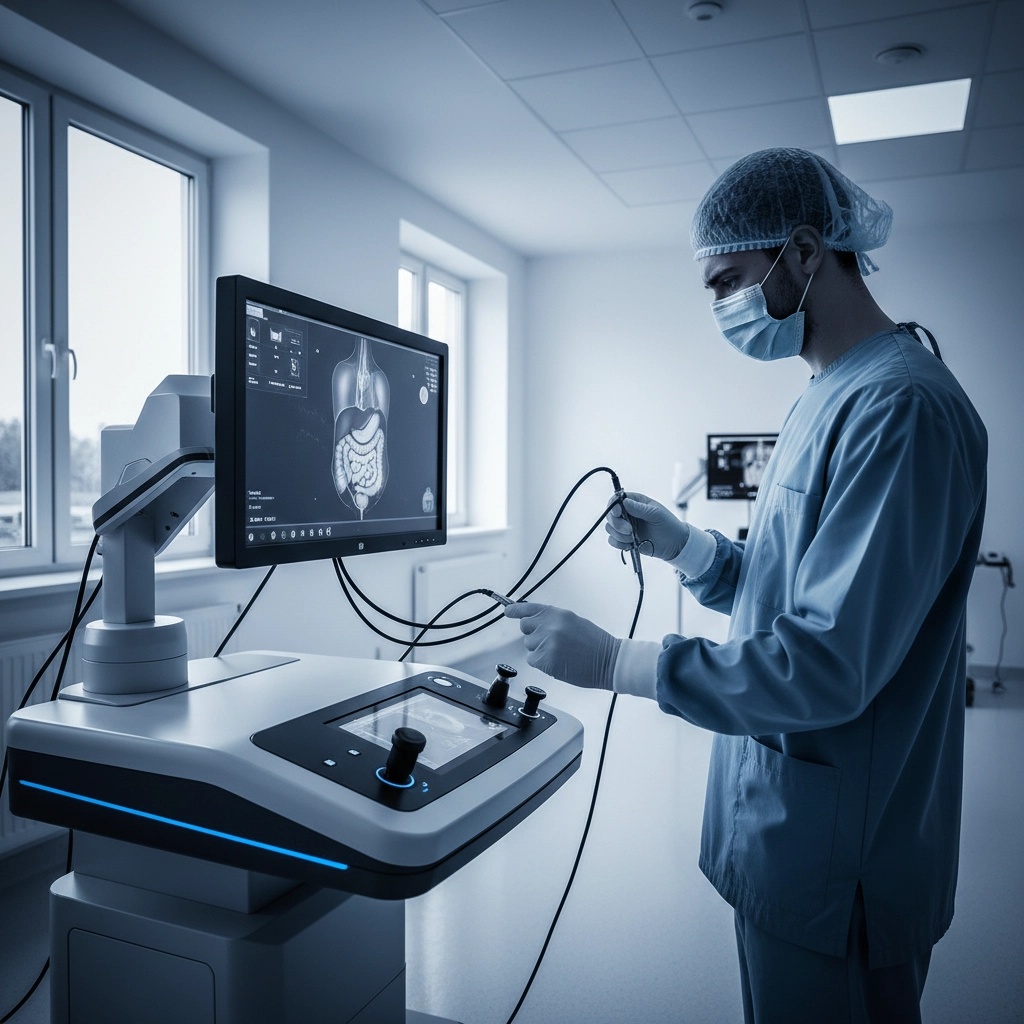
Medical education represents one of the most successful applications of simulation-based learning. Virtual patient simulations allow medical students to practice diagnostic procedures, surgical techniques, and emergency response protocols without risking patient safety. These systems provide immediate feedback and enable repetitive practice of complex procedures until mastery is achieved.
Advanced medical simulators now incorporate haptic feedback technology, allowing students to feel resistance and texture during virtual procedures. This tactile component bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, preparing medical professionals for real-world patient interactions.
Business and Management Education
Corporate training programs increasingly rely on simulation-based methodologies to prepare employees for various workplace scenarios. Business simulations can replicate market conditions, crisis management situations, and complex organizational challenges, allowing employees to develop crucial skills in strategic thinking and leadership.
Examples include simulations for customer service scenarios, negotiation training, crisis management protocols, team leadership development, and complex problem-solving situations. These programs typically result in measurable improvements in employee performance and organizational effectiveness.
STEM Education Transformation
Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics education benefits significantly from simulation-based approaches. Virtual laboratories enable students to conduct experiments in controlled environments that are safer and more cost-effective than traditional laboratory settings. Chemistry simulations allow exploration of dangerous reactions, physics simulations demonstrate complex theoretical concepts, and engineering simulations enable testing of design concepts without material costs.
Key Components of Effective Simulation Learning
Modern educational simulations incorporate several essential characteristics that maximize their educational impact. Guided participation ensures that instructors can establish simulation parameters and provide support throughout the learning process, with most systems offering pause functions that allow performance evaluation at critical moments.
Environmental realism creates virtual spaces that accurately mirror real-world settings, from laboratory environments to complex industrial facilities. These controlled environments provide security where learners can experiment and learn from mistakes without facing actual consequences or safety risks.

Role-playing elements place learners in specific positions within simulated scenarios, creating engagement that makes participants feel authentically present in the situation. This approach fosters collaborative skills and helps learners appreciate diverse perspectives from team members and stakeholders.
Structured reflection opportunities allow participants to analyze their experiences systematically, identifying successful strategies and lessons learned from their simulation participation. Finally, scenario-based challenges present learners with problems requiring solution or events demanding response within controlled environments with predetermined parameters such as available resources and time constraints.
Technological Innovations Driving the Future
The future of simulation-based education is being shaped by emerging technologies that promise increasingly immersive and effective learning experiences. Virtual reality and augmented reality technologies create highly immersive interactive experiences that allow learners to explore and manipulate virtual environments with unprecedented realism.
Artificial intelligence integration represents another significant advancement, enabling personalized learning experiences through machine learning algorithms that adapt to individual learner needs, preferences, and performance patterns. This personalization enhances both learning effectiveness and retention by accommodating specific learning styles and optimal pacing for each student.
Adaptive learning systems promise to deliver completely tailored educational programs that adjust content difficulty, presentation style, and assessment methods based on individual progress and performance metrics. These systems continuously monitor learner engagement and comprehension, making real-time adjustments to optimize educational outcomes.
Implementation Challenges and Strategic Solutions
Despite significant benefits, simulation-based learning systems face implementation challenges that organizations must address strategically. Initial development costs can be substantial, requiring significant investment in technology infrastructure, content creation, and system implementation. Additionally, creating high-quality simulations demands extensive planning, development, and testing phases that can extend project timelines considerably.
However, simulation-based learning often proves cost-effective over extended periods, as these systems can be utilized repeatedly without incurring additional variable costs once developed. The initial investment typically becomes offset by improved learning outcomes, reduced need for physical resources, and the ability to train large numbers of learners simultaneously.
Organizations implementing simulation-based learning must also consider technical support requirements, user training needs, and ongoing system maintenance. Successful implementation requires comprehensive change management strategies that address both technological and cultural adaptation challenges.

Future Outlook and Strategic Recommendations
The transformation of education through simulation technology represents a fundamental shift toward more engaging, effective, and practical learning experiences. As technology continues advancing and implementation costs decrease, simulation-based learning is positioned to become an increasingly integral component of educational systems across all levels and industries.
Educational institutions and training organizations should begin evaluating simulation-based learning opportunities within their specific contexts, identifying areas where traditional methods fall short of desired outcomes. Pilot programs can provide valuable insights into implementation requirements and effectiveness measures before full-scale adoption.
The integration of simulation-based learning with traditional educational methods offers the most promising approach for immediate implementation. This hybrid model leverages the strengths of both methodologies while addressing their respective limitations, creating comprehensive learning experiences that maximize educational effectiveness.
Organizations that proactively adopt simulation-based learning methodologies position themselves advantageously in an increasingly competitive educational landscape. The demonstrated benefits of improved learning outcomes, enhanced skill development, and increased learner engagement make simulation-based education not merely an option, but an essential component of future-ready educational strategies.







